Describe How a Vaccine Protects Against Disease
This fact sheet explains how the body fights infection and how vaccines work to protect people by producing immunity. Langel PhD demonstrated the potential of a COVID vaccine that works through the mucosal tissue to.

How Vaccines Work British Society For Immunology
Protect your child from 16 diseases with vaccines.

. 8 hours agoA COVID-19 vaccine designed to be taken orally not only protects against the disease but also decreases the airborne spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus to other close contacts according to a study conducted in animals. Vaccines are very effective and theyre the best protection against many serious diseases. By tailoring the bodys own immune defenses vaccines provide protection against many infectious diseases either by blocking them entirely or reducing the severity of their symptoms.
Skip directly to site content Skip directly to page options Skip directly to A-Z link. They then leave behind memory cells that can instigate a defense should the pathogen return. Vaccines can prevent contagious diseases that once killed or harmed many infants children and adults.
Learn more about these diseases and the vaccines that prevent them. How vaccines prevent infectious diseases Vaccines are medicines that help to protect you and your family from infectious diseases. The study led by Duke researcher Stephanie N.
Unlike antibiotics or other medicines that treat infections vaccines prevent infections. Vaccines can give you side effects but these go away. Measles mumps and rubella.
Contain a dead or altered form of the disease-causing pathogen which is introduced into the body. Recommended childhood vaccines help protect against serious diseases. Vaccines reduce risks of getting a disease by working with your bodys natural defenses to build protection.
The FDA ensures that the. A vaccine is a substance that is introduced into the body to stimulate the bodys immune response. Diphtheria can affect people of all ages but can be prevented with vaccination.
Vaccines greatly reduce the risk of infection by working with the bodys natural defenses to safely develop immunity to disease. Stevica Mrdja EyeEm Getty Images. Vaccines prevent diseases that can be dangerous or even deadly.
This makes it difficult for the virus or bacteria to spread because there are so few unvaccinated people left to infect. It is given to prevent an infectious disease from developing and the person becoming ill. That means that vaccines help protect you from diseases without ever having to risk the serious and sometimes deadly consequences of getting sick from those diseases.
Symptoms include a sore throat and breathing problems. VirusesBacteria and Your Immune System. Vaccines help your immune system recognise viruses and bacteria and destroy them quickly.
Vaccines are made from microbes that are dead or inactive so. Most people who get vaccinated will have immunity protection against the disease. That means even people who cant get vaccinated will have some protection from getting sick.
Rubella infection in children and adults is usually mild but in pregnant women it can cause miscarriage stillbirth infant death or birth defects. Recognizes the invading germ such as the virus or bacteria. Making antibodies against the germ.
Vaccines work by helping people safely imitate natural infections. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Through herd immunity vaccinations also protect people who.
The meningococcal conjugate vaccine that protects against meningitis also doesnt work as well over time. These dead or altered pathogens carry a specific antigen. The vaccine protects against complications like pneumonia meningitis or infection of the blood caused by the bacteriumStreptococcus pneumoniae.
Vaccines are injections shots liquids pills or nasal sprays that you take to teach your bodys immune system to recognize and defend against harmful germs. So you need different vaccines to protect against different germs. How Vaccines Work.
Herd immunity can effectively stop the spread of a disease. Antibodies are proteins produced naturally by the immune system to fight disease. It remains important for children to be immunised at this time.
To do this certain molecules from the pathogen must be introduced into the body to trigger an immune response. Herd immunity happens when a big enough part of a population gets vaccinated against a virus or bacteria. After getting vaccinated you develop immunity to that disease without having been infected with the germ.
The research published in the journal Science Translational Medicine demonstrates the potential of the vaccine to work through. For example there are vaccines to protect against diseases caused by. This combined vaccine protects children from three viral diseases.
If enough people get sick it can lead to an outbreak. When peoples immunity drops it can lead to new disease outbreaks unless more people in. Vaccines are responsible for eliminating smallpox and reducing by 95 percent or more many of the common childhood diseases like diphtheria measles and polio which once killed hundreds of thousands.
Treatment includes antibiotics and diphtheria anti-toxin. Complications can include meningitis swollen testicles and deafness. CDC twenty four seven.
When viruses or bacteria germs invade your body they attack and multiply. Even now there are 15 million peoplemostly children in the developing. Vaccines protect you from specific germs.
In this section youll learn more about. But when enough people are vaccinated against a certain disease the germs cant travel as easily from person to person and the entire community is less likely to get the disease. How vaccines protect you.
But not everyone can be vaccinated. Vaccines are one of the greatest advancements in the history of public health. Diphtheria is a contagious disease spread by an infected persons coughing sneezing or open wounds.
Viruses like the ones that cause the flu and COVID-19. Bacteria including tetanus diphtheria and pertussis. In this way the body is trained to fight the specific disease-causing organism building up memory of the pathogen so as to rapidly fight it if and when exposed in the future.
When someone is vaccinated they are very likely to be protected against the targeted disease. When you get a vaccine your immune system responds. These molecules are called antigens and they are present on all viruses and bacteria.
A vaccine works by training the immune system to recognize and combat pathogens either viruses or bacteria. Once we have been immunised our bodies are better able to fight these diseases if we come into contact with them. Immunisation is a way of protecting against serious diseases.
Mumps can cause headache malaise fever and swollen salivary glands.

How Mrna Vaccines Protect You Against Covid 19 Consilium

How Vaccines Work British Society For Immunology
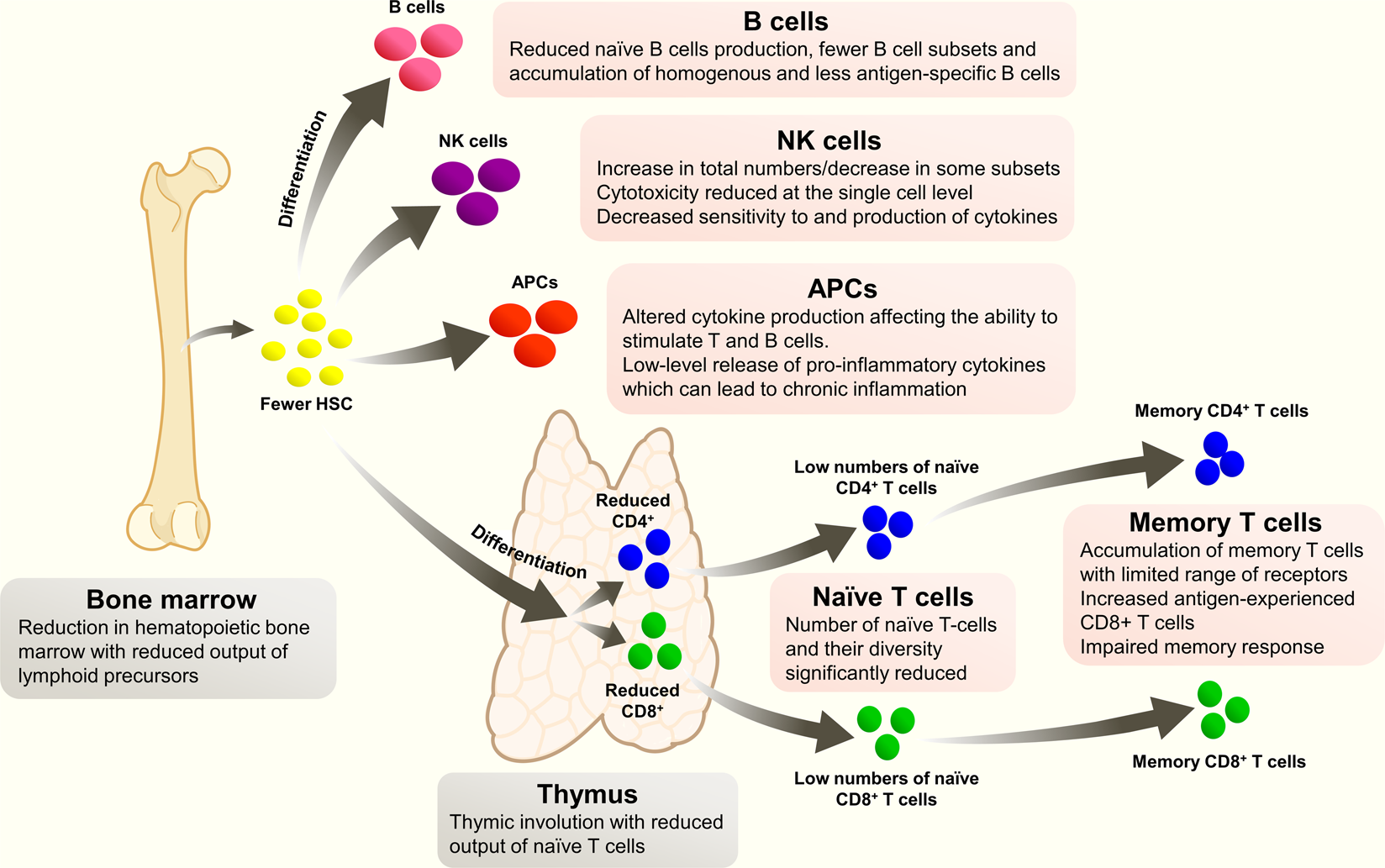
Vaccination As A Preventative Measure Contributing To Immune Fitness Npj Vaccines
No comments for "Describe How a Vaccine Protects Against Disease"
Post a Comment